What is personal finance?
Personal finance involves managing your money through budgeting, saving, investing, and making informed financial decisions to achieve financial security and independence. It encompasses all financial activities that an individual or family undertakes, including income generation, expenditure, savings, investments, debt management, and insurance coverage.
In simpler terms, personal finance is about how you handle your money wisely today, ensuring it supports your goals tomorrow. Whether planning for short-term goals like buying a smartphone or long-term milestones like purchasing a house or preparing for retirement, mastering personal finance is essential.
Importance of Personal Finance in India
Personal finance has grown increasingly significant in India, a country witnessing rapid economic changes, increasing inflation, and a dynamic financial landscape. Here’s why understanding personal finance is crucial for every Indian:
-
Economic Stability: Proper financial planning ensures you remain stable even during economic downturns or unexpected events, protecting you and your family against financial distress.
-
Wealth Creation: Effective personal finance management enables wealth accumulation over time through savings and prudent investment strategies, allowing for greater financial freedom.
-
Inflation Management: With India’s inflation rates often fluctuating, understanding personal finance helps maintain your purchasing power by wisely investing and saving.
-
Debt Reduction: Knowledge of personal finance can prevent overwhelming debt by teaching responsible borrowing and timely repayments, keeping your financial health intact.
-
Retirement Planning: A strong foundation in personal finance is essential for retirement planning, ensuring financial independence and peace of mind during your golden years.
-
Better Financial Decisions: Educated decisions about investments, loans, insurance, and expenses lead to reduced risks and maximised returns, enhancing your overall financial well-being.
Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Your Money
Step 1: Set Clear Financial Goals
Establishing clear financial goals is a critical first step toward effective money management. Financial goals help define your financial direction, guide your spending habits, and shape your overall financial strategy.

Short-term vs. Long-term Goals
Understanding the difference between short-term and long-term financial goals is essential:
-
Short-term goals: These typically span from a few months to a few years and might include building an emergency fund, paying off debt, or saving for a vacation.
-
Long-term goals: These span several years or decades and include purchasing a home, funding your child’s education, or planning for retirement.
Clearly distinguishing these goals helps allocate your resources efficiently and ensures that immediate financial needs don’t overshadow future aspirations.
SMART Criteria for Financial Planning
Applying the SMART criteria ensures your financial goals are achievable and effective:
-
Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve (e.g., “save ₹50,000 for an emergency fund”).
-
Measurable: Establish clear benchmarks to track progress (e.g., “save ₹4,000 per month”).
-
Achievable: Set realistic and attainable goals based on your current financial situation.
-
Relevant: Ensure goals align with your broader financial objectives and life priorities.
-
Time-bound: Set clear deadlines to foster urgency and discipline (e.g., “within 12 months”).
Step 2: Budgeting for Beginners
Creating and maintaining a monthly budget is foundational to achieving financial stability and meeting your financial goals. Here’s a simple guide tailored for beginners to help you get started:
How to Create a Monthly Budget
Follow these easy steps to set up your monthly budget:
-
List Your Income: Note down all sources of monthly income, including salary, freelance earnings, and other revenue streams.
-
Track Your Expenses: For a month, document all your spending to understand your habits clearly.
-
Categorise Your Spending: Group expenses into categories like housing, food, transportation, entertainment, savings, and debt repayments.
-
Set Limits: Allocate specific amounts to each category based on your income and spending insights.
-
Review and Adjust: Regularly review your budget to ensure you’re on track and adjust as necessary to reflect changes in income or expenses.
Essential vs. Non-essential Expenses
Understanding the difference between essential and non-essential expenses is critical:
-
Essential Expenses: These are necessary costs, including rent or mortgage payments, groceries, utilities, insurance premiums, and healthcare.
-
Non-essential Expenses: These include discretionary spending on entertainment, dining out, travel, and luxury items.
Differentiating these clearly helps prioritise spending and ensure your basic needs and financial goals are consistently met.
Budgeting Tools and Apps Popular in India
Utilise these widely popular budgeting tools and apps to streamline your budgeting process:
-
Walnut: Automatically tracks spending and offers insights into your financial habits.
-
Money View helps manage bills, track expenses, and provide real-time spending analysis.
-
ETMoney: A comprehensive tool for expense tracking, investment management, and financial goal planning.
-
Goodbudget: Ideal for envelope budgeting, helping you allocate your income effectively.
Step 3: Saving Money Effectively
Saving money is a crucial aspect of achieving financial security and independence. Here’s how you can save effectively to secure your financial future:

Importance of Emergency Funds
An emergency fund acts as a financial safety net, helping you manage unexpected expenses like medical emergencies, sudden job loss, or urgent home repairs. Ideally, your emergency fund should cover at least three to six months of living expenses. Having this reserve provides peace of mind and prevents reliance on high-interest debt during emergencies.
Saving Strategies Suitable for Indian Incomes
Here are practical saving strategies tailored for individuals earning typical Indian incomes:
-
Pay Yourself First: Prioritise savings by automatically transferring a fixed portion of your income into a savings account as soon as you receive your pay cheque.
-
Start Small: Even small, regular savings can accumulate significantly over time. Begin with what you can comfortably set aside and gradually increase the amount.
-
Utilise Tax-Saving Instruments: Invest in options like Public Provident Fund (PPF), Employee Provident Fund (EPF), and National Savings Certificates (NSC) that offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
-
Cut Unnecessary Expenses: Regularly review your budget and identify non-essential expenditures to redirect funds into savings.
-
Monitor Spending Habits: Regular tracking can reveal patterns that you can adjust to enhance your savings.
Top Savings Accounts and Fixed Deposits in India
Consider these popular savings accounts and fixed deposit options known for attractive interest rates and reliability in India:
Savings Accounts:
-
Kotak Mahindra Bank 811 Account: High-interest savings account with digital banking convenience.
-
IDFC First Bank Savings Account: Offers competitive interest rates and minimal balance requirements.
-
DBS Bank DigiSavings: Known for attractive interest rates, easy digital access, and hassle-free banking.
Fixed Deposits:
-
State Bank of India (SBI) FD: Offers secure and competitive returns with flexibility in tenures.
-
HDFC Bank Fixed Deposit: Known for stable returns, ease of opening, and robust customer service.
-
Bajaj Finance Fixed Deposit: Provides higher interest rates compared to traditional banks, making it suitable for maximising returns.
Step 4: Getting Started with Investments
Investing your money wisely can accelerate your journey toward financial independence and wealth creation. Here’s a beginner-friendly guide to help you understand the basics and make informed investment choices:
Basics of Investing: Stocks, Mutual Funds, Bonds
-
Stocks: Represent ownership in a company. Investing in stocks offers high return potential but comes with greater risks due to market volatility.
-
Mutual Funds: Pool money from multiple investors and invest in a diversified portfolio of assets like stocks or bonds. Managed by professionals, mutual funds are ideal for beginners due to lower risk and ease of access.
-
Bonds: Fixed-income instruments issued by governments or corporations. Bonds provide predictable returns and are suitable for conservative investors seeking stability.
Mutual Funds vs. Direct Stock Investing
Understanding the differences between mutual funds and direct stock investments helps make smarter financial decisions:
Mutual Funds
-
Professionally managed, diversified portfolios
-
Lower risk due to spread-out investments
-
Suitable for beginners or time-constrained individuals
Direct Stock Investing
-
Higher return potential with informed stock picking
-
Requires significant market knowledge and research
-
Higher risk due to market fluctuations and concentrated holdings
Investment Platforms and Apps for Beginners
Get started conveniently with these trusted Indian investment apps:
-
Groww: Beginner-friendly UI; invest in mutual funds, stocks, and digital gold.
-
Zerodha is ideal for direct stock investments; it offers advanced tools and low broking.
-
Paytm Money: An easy-to-use platform for mutual funds with integrated financial planning.
-
ETMoney: A full-suite app with mutual funds, insurance, and goal-based investing.
Choosing the right investment strategy based on your goals, risk appetite, and time horizon is the key to building sustainable wealth.
Step 5: Managing and Reducing Debt
Effectively managing and reducing debt is essential for achieving financial stability and long-term prosperity. Here’s how you can better understand and tackle your debts:

Understanding Different Types of Debt
Each debt type requires different strategies:
-
Personal Loans: Unsecured and versatile loans often used for emergencies, carrying higher interest rates.
-
Credit Cards: Convenient but risky if not repaid in full; known for high-interest charges.
-
Home Loans: Long-term, secured loans with relatively lower interest rates, used for real estate purchases.
Best Practices to Reduce Debt Quickly
Use these methods to reduce your debt burden efficiently:
-
Prioritise High-Interest Debt: Pay off debts like credit cards first to reduce cumulative interest.
-
Increase Repayment Amounts: Pay more than the minimum to cut down the principal faster.
-
Debt Consolidation: Combine multiple debts into one with a lower interest rate to simplify payments.
-
Avoid New Debt: Postpone new credit until current liabilities are under control.
Debt Management Resources in India
Explore these Indian resources for managing your debt wisely:
-
Credit Information Bureaus (e.g., CIBIL): Get reports and monitor credit scores to maintain financial discipline.
-
Financial Counselling Services: DMCC and other NGOs provide advice and customised debt management plans.
-
Bank Advisory Services: Many banks offer restructuring plans and expert consultation for struggling borrowers.
Step 6: Planning for Retirement
Planning early for retirement is important because it guarantees financial independence and comfort during your later years.
Why Retirement Planning Matters Early
Starting early allows you to benefit from compound interest, which helps your money grow exponentially. It also gives you more time to
-
Adjust your investments
-
Manage risks effectively
-
Build a substantial retirement corpus with less financial stress
Options for Retirement Savings: NPS, EPF, PPF
Here are some of the most trusted and widely used retirement savings tools in India:
-
National Pension Scheme (NPS): A government-backed, tax-efficient plan with flexible investment choices and long-term wealth generation.
-
Employee Provident Fund (EPF): Mandatory for salaried employees; offers high interest rates and tax-free maturity.
-
Public Provident Fund (PPF): Ideal for conservative investors seeking stable returns and Section 80C tax benefits.
Calculating How Much You’ll Need for Retirement
Estimate your required retirement corpus based on:
-
Expected monthly expenses
-
Inflation rate
-
Life expectancy
-
Medical and healthcare costs
Use online retirement calculators for a tailored plan that aligns with your future goals.
Financial Strategies for Building Wealth
Applying sound strategies ensures sustainable financial growth and long-term wealth accumulation.
Diversification: Why It’s Essential
Diversifying across asset classes—stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate—minimises risk and balances portfolio performance over time.
Automating Savings and Investments
Set up automation through:
-
Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs)
-
Recurring Deposits (RDs)
-
Auto transfers to savings accounts
Automation ensures discipline and consistency without needing manual effort every month.
How to Periodically Review Your Financial Plan
Reevaluate your financial plan at least once a year for the following reasons:
-
Align with life changes (job change, marriage, children)
-
Adjust for new goals
-
Adapt to market conditions
This habit keeps your strategy optimised and relevant.
Common Personal Finance Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding these common missteps can help maintain long-term financial health and resilience:

Overspending
Living beyond your means leads to debt and stagnated savings. Track expenses and stick to a well-planned monthly budget.
Not Having an Emergency Fund
Without emergency savings, any unexpected expense can derail your finances. Aim to save 3–6 months of essential living expenses in a separate fund.
Avoiding Investments
Storing all money in savings accounts won’t beat inflation. Invest small amounts regularly in mutual funds, PPF, or gold ETFs.
Ignoring Insurance Needs
Without adequate life and health insurance, you risk significant financial exposure during emergencies. Choose plans that align with your lifestyle and family needs.
FAQ Section
What are the first steps to manage personal finance in India?
Start by:
-
Creating a monthly budget
-
Building an emergency fund
-
Setting short- and long-term goals
-
Investing in simple tools like EPF, PPF, and mutual funds
How much money should I save each month?
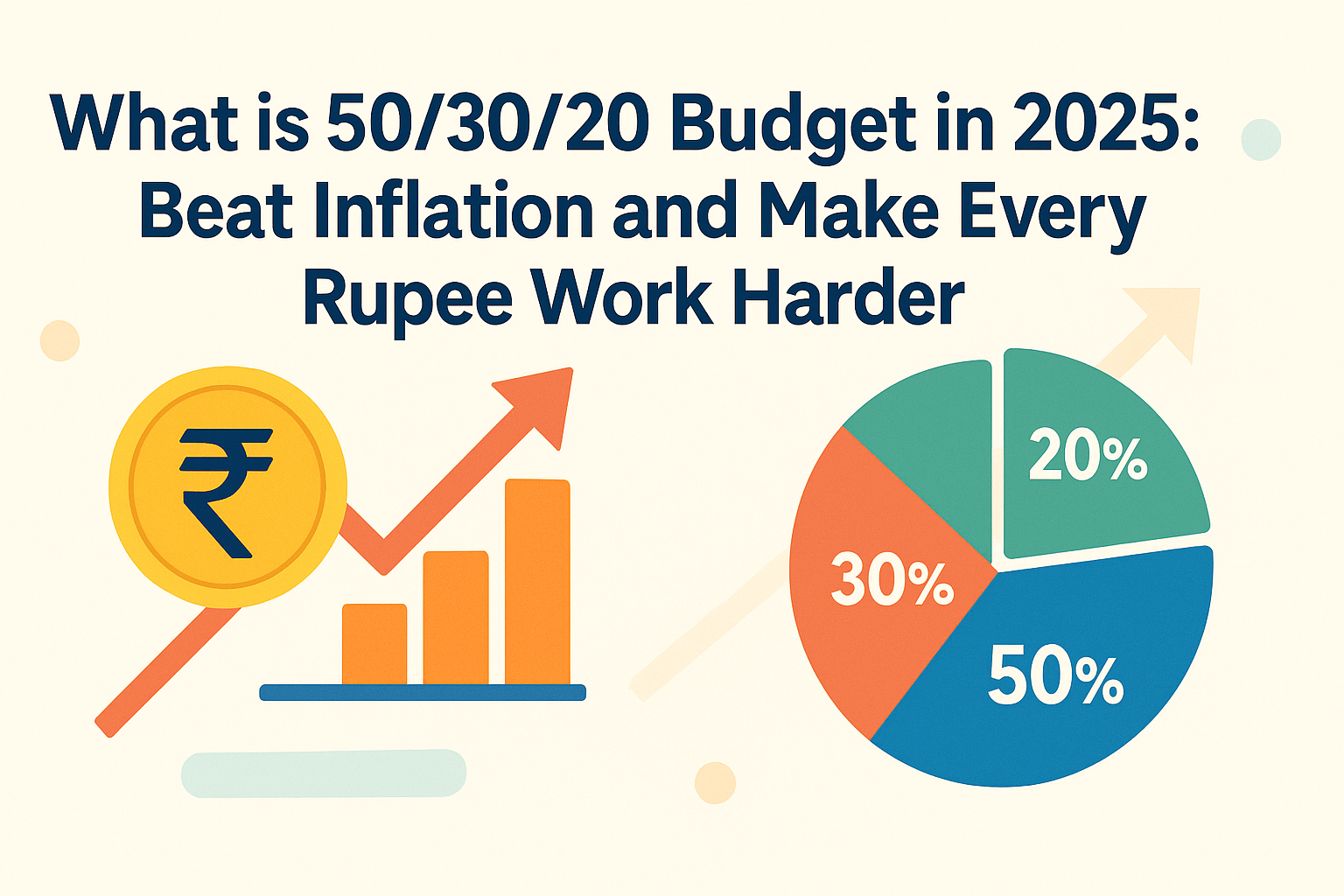
Try to save at least 20% of your monthly income. Adjust based on expenses, goals, and liabilities.
Is investing in mutual funds safe for beginners?
Yes, mutual funds are ideal for beginners due to
-
Professional management
-
Diversified risk
-
Multiple types suited to all risk levels
What is the best way to track personal expenses?
Use Indian budgeting tools like
-
Walnut
-
Money View
-
ETMoney
These apps categorise expenses and help monitor cash flow easily.
How do I start investing with a small salary in India?
Start with:
-
SIPs in low-risk mutual funds
-
Recurring deposits
-
Government-backed schemes like PPF or NPS
You can begin with as little as ₹500 per month.
Conclusion
By following this structured guide—from setting goals and budgeting to investing, debt management, and retirement planning—you’ll establish a solid foundation in personal finance.
Maintain consistency and stay informed, and you will successfully navigate your journey from poverty to wealth.